Harnessing Efficiency: Warehouse Automation in the Solar Energy Revolution
In today's rapidly advancing world, the solar energy sector stands at the forefront of sustainable innovation.
Read More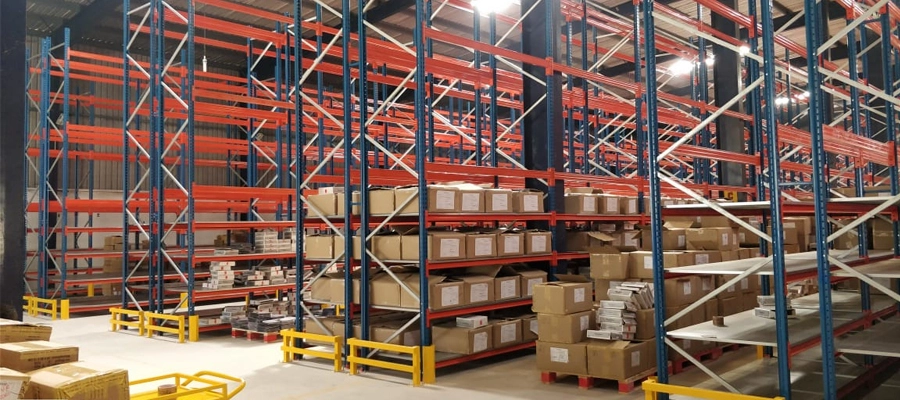
Operating a safe and secure warehouse reduces the chance of occupational and on-the-job injuries, as well as the never-ending list of dangers and costs that come with them. Here are some guidelines for operational aspects relevant to the structural safety of storage systems because these systems operate with heavy Material handling equipment working in close condition to the storage equipment.
These guidelines help you minimize the risk and consequences of unsafe operation or damage to the structure
Person Responsible for Storage Equipment Safety
The person responsible for storage equipment safety shall be aware of the nature of the operations in the warehouse and the associated dangers based on a risk assessment, as well as the precautions that are taken to prevent or limit the dangers, using instructions or signs
Safety Load Warning Charts
Load Capacity Charts and other important information related to the racking installation should be posted in the storage area. Heavier unit loads than those prescribed by the specifier must be notified by a warning notice.
All operating persons within the warehouse are to be trained in safe working practices. Forklift truck drivers should be trained properly to use the system safely and also about the right pallet to be used, load capacity of rack, loading and unloading method on racks. They should be certified/licensed
Spillage of Goods
Spillage of goods occurs when unstable goods are loaded.
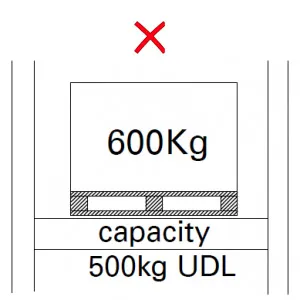
Load
Heavier unit loads than those prescribed by the specifier and shown on the load warning notice should not be placed in the storage equipment.
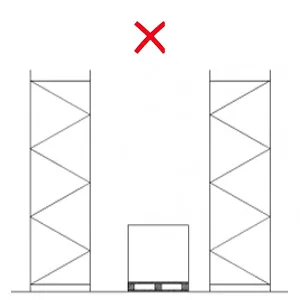
Aisle Obstructions
Pallets placed on the aisle affect the MHE movement. The operating aisle width should be maintained with sufficient clearance for smooth MHE movement.
Pallet Damages
Damaged Pallets, broken or cracked boards, protruding nails, or other deficiencies can damage the rack beams. Use only pallets of the correct size and in good working condition. The pallet type, dimensions, tolerances, quality, and design should be suitable for safe operation and storage on the particular storage equipment.
Load Stability
The load must be uniformly distributed and properly stacked on the pallet.

Material Handling Equipment
Material handling equipment such as Forklift, Reach Trucks, Stacker Cranes should have the capacity to lift the specified load at the required height and also be suitable for the available aisle width. Since MHE affects the safety of the rack structure, proper MHE maintenance and skilled operators are required.
The pallet must be picked up square to the forks. The fork length should be sufficient to support the pallet and it should not be too long or short than the load.
User Responsibility
The user is responsible for the safety of persons working in the area of storage equipment and for safe working conditions. The user must make sure that the MHE is operated carefully and overall dimension and weight of the unit load should not exceed the limitations in the specification. The pallet should be kept only on the loading member and other than that there should not be any contact or hitting between the fork truck or the pallet with any part of storage equipment.
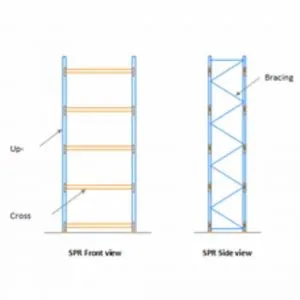
SPR is the most widely used storage system for fast-moving palletized loads. It is the most economical form of pallet racking because it provides 100% selective storage. It offers direct access to all pallets with great load flexibility. It consists of upright frames interconnected by cross beams in the horizontal direction and the MHE is driven into the aisle in between the racks to deposit and retrieve pallets. Moreover, the racking configuration can be easily modified and extended
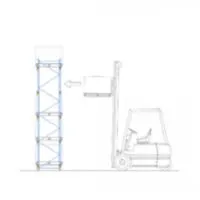
Loading the System
When a pallet is placed into the SPR, the loading sequence shall ensure that there is no contact with the racks structure or a unit load already stored during the placement or retrieval operation. Forklift drives with the pallet and takes up the position in front of the vacant storage location.
Forks shall be horizontal and the pallet or SKU shall be lifted clear from the top of the support beam. Pallet shall be positioned concentrically in the depth of the rack concerning the pallet beams. After placement, the fork entry of the pallet shall be visible to the truck operator.
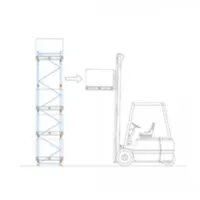
Unloading the System
The forklift truck approaches the rack squarely and raises the forks to the required storage level and inserts the forks into the required pallet.
Carefully lift the pallet just clear of the cross beams, ensuring it is not raised too far thus hitting the above level cross beam. Remove the pallet clear of the rack before lowering the forks to the correct traveling position before moving off.
Improper and Proper Entry Method
The forklift should not approach the rack at an angle and realign after handling the pallet. Forklift trucks should approach squarely towards the rack.
Clearance Required
The horizontal and vertical clearances for pallet and rack shall be greater than or equal to the values shown in the below table
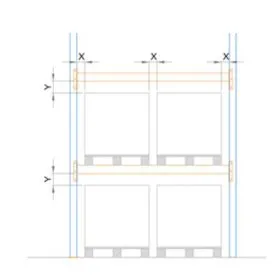
| Beam Height from ground to beam level (mm) | X(mm) | Y(mm) |
| 3000 | 75 | 75 |
| 6000 | 75 | 100 |
| 9000 | 75 | 125 |
| 13000 | 100 | 150 |
Safety Lock Pin
Safety pins are used to prevent accidental dislodging of beams and if missing should be replaced. Alternatively, the beam can be bolted to the upright.

Storage equipment should be checked frequently and repair should be carried out in a timely and effective manner. Damage can be to the upright bracing beam or any other part of the system.
Measurement of Damage to Upright, Bracing, and Beam
For an upright bend in the direction of the rack beam spans, the maximum gap between the upright and straight edge shall not exceed 5 mm.
Straight edge 1,0 m long is placed in contact with a flat surface on the concave side of the damaged member such that the damaged area lies central, as near as possible, to the length of the straight edge.
For an upright bent in the direction of the rack beam spans, the maximum gap between the upright and straight edge shall not exceed 5,0 mm.
For an upright bent in the plane of the frame bracing, the maximum gap between the upright and straight edge shall not exceed 3,0 mm.
Beams should not deflect (Bend in the center) more than the L/200, where L = the distance between two beam supports.
For an upright that has been damaged such that there is a simultaneous bend in both longitudinal and lateral directions the left-to-right and the front-to-back deformation shall be measured and treated separately and the appropriate 5,0 mm and 3,0 mm, limits observed.
For bracing members bent in either plane, the gap between the straight edge and the bracing member shall not exceed 10,0 mm over a 1.0 m gauge length or pro-rata for shorter bracings where a 1,0 m gauge length is not practical.
Green level – Require surveillance
Orange Risk – Hazardous damage requiring action as soon as possible
Red Risk – Very serious damage requiring immediate action